Portal:India
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
Introduction


India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country in the world by area and the most populous country. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. (Full article...)
 Featured article – show another
Featured article – show another
-
Image 1Mother India is a 1957 Indian epic drama film, directed by Mehboob Khan and starring Nargis, Sunil Dutt, Rajendra Kumar and Raaj Kumar. A remake of Khan's earlier film Aurat (1940), it is the story of a poverty-stricken village woman named Radha (Nargis), who in the absence of her husband, struggles to raise her sons and survive against a cunning money-lender amidst many troubles.
The title of the film was chosen to counter American author Katherine Mayo's 1927 polemical book Mother India, which vilified Indian culture. Mother India metaphorically represents India as a nation in the aftermath of its independence in 1947, and alludes to a strong sense of Indian nationalism and nation-building. Allusions to Hindu mythology are abundant in the film, and its lead character has been seen as a metonymic representation of an Indian woman who reflects high moral values and the concept of what it means to be a mother to society through self-sacrifice. While some authors treat Radha as the symbol of women's empowerment, others see her cast in female stereotypes. The film was shot in Mumbai's Mehboob Studios and in the villages of Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Uttar Pradesh. The music by Naushad introduced global music, including Western classical music and orchestra, to Hindi cinema. (Full article...) -
Image 2Pather Panchali (pronounced [pɔtʰer pãtʃali] transl. Song of the Little Road) is a 1955 Indian Bengali-language drama film written and directed by Satyajit Ray in his directoral debut and produced by the Government of West Bengal. It is an adaptation of Bibhutibhushan Bandyopadhyay's 1929 Bengali novel of the same name and features Subir Banerjee, Kanu Banerjee, Karuna Banerjee, Uma Dasgupta, Pinaki Sengupta and Chunibala Devi in major roles. The first film in The Apu Trilogy, Pather Panchali depicts the childhood travails of the protagonist Apu and his elder sister Durga amidst the harsh village life of their poor family.
The film was shot mainly on location, had a limited budget, featured mostly amateur actors, and was made by an inexperienced crew. Lack of funds led to frequent interruptions in production, which took nearly three years, but the West Bengal government pulled Ray out of debt by buying the film for the equivalent of $60,000, which it turned into a profit of $700,000 by 1980. The sitar player Ravi Shankar composed the film's soundtrack and score using classical Indian ragas. Subrata Mitra was in charge of the cinematography while editing was handled by Dulal Dutta. Following its premiere on 3 May 1955 during an exhibition at New York's Museum of Modern Art, Pather Panchali was released in Calcutta the same year to an enthusiastic reception. A special screening was attended by the Chief Minister of West Bengal and the Prime Minister of India. (Full article...) -
Image 3Aravan worshipped at Sri Mariamman Temple, Singapore. A cobra hood is sheltering Aravan's head.
Iravan also known as Iravat and Iravant, is a minor character from the Hindu epic Mahabharata. The son of Pandava prince Arjuna (one of the main heroes of the Mahabharata) and the Naga princess Ulupi, Iravan is the central deity of the cult of Kuttantavar (Kuttandavar) which is also the name commonly given to him in that tradition—and plays a major role in the sect of Draupadi. Both these sects are of Tamil origin, from a region of the country where he is worshipped as a village deity and is known as Aravan. He is also a patron god of well-known transgender communities called Alis (also Aravani in Tamil, and Hijra throughout South Asia).
The Mahabharata portrays Iravan as dying a heroic death on the 8th day of the 18-day Kurukshetra War (Mahabharata war), the epic's main subject. However, the South Indian traditions have a supplementary practice of honouring Aravan's self-sacrifice to the goddess Kali to ensure her favour and the victory of the Pandavas in the war. The Kuttantavar tradition focuses on one of the three boons granted to Aravan by the god Krishna in honour of this self-sacrifice. Aravan requested that he be married before his death. Krishna satisfied this boon in his female form, Mohini. In Koovagam, Tamil Nadu, this incident is re-enacted in an 18-day festival, first by a ceremonial marriage of Aravan to Alis (hijra) and male villagers (who have taken vows to Aravan) and then by their widowhood after ritual re-enactment of Aravan's sacrifice. (Full article...) -
Image 4
The Indian roller (Coracias benghalensis) is a bird of the family Coraciidae. It is 30–34 cm (12–13 in) long with a wingspan of 65–74 cm (26–29 in) and weighs 166–176 g (5.9–6.2 oz). The face and throat are pinkish, the head and back are brown, with blue on the rump and contrasting light and dark blue on the wings and tail. The bright blue markings on the wing are prominent in flight. The sexes are similar in appearance. Two subspecies are recognised.
The Indian roller occurs widely from West Asia to the Indian subcontinent. Often found perched on roadside trees and wires, it is common in open grassland and scrub forest habitats, and has adapted well to human-modified landscapes. It mainly feeds on insects, especially beetles. The species is best known for the aerobatic displays of males during the breeding season. Adult males and females form pair bonds and raise the young together. The female lays 3–5 eggs in a cavity or crevice, which is lined with a thin mat of straw or feathers. The roller is the state bird of three Indian states. It is listed as a species of least concern on the IUCN Red List. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Nyctibatrachus major, the Malabar night frog, large wrinkled frog, or Boulenger's narrow-eyed frog is a species of frog in the family Nyctibatrachidae, commonly known as the robust frogs. It was described in 1882 by the zoologist George Albert Boulenger, and is the type species of the genus Nyctibatrachus. It is a large frog for its genus, with an adult snout–vent length of 31.5–52.0 mm (1.24–2.05 in) for males and 43.7–54.2 mm (1.72–2.13 in) for females. It is mainly brownish to greyish in colour, with a dark greyish-brown upperside, a greyish-white underside, and light grey sides. It also has a variety of grey or brown markings. When preserved in ethanol, it is mostly greyish-brown to grey, with whitish sides. Sexes can be told apart by the presence of the femoral glands (bulbous glands near the inner thigh) in males.
The species is endemic to the Western Ghats mountain range of India, where it is found in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. Adults inhabit fast-moving forest streams at elevations of up to 900 m (3,000 ft) and have highly specific habitat requirements. Adults are mostly found in or near water and are nocturnal; subadults can be found during both the night and day. Its diet mainly consists of other frogs and insect larvae. Over a period of several days or weeks, females lay multiple small clutches of eggs on leaves and rocks overhanging water; tadpoles drop into the water below on hatching. The species is currently classified as being vulnerable on the IUCN Red List owing to its small and fragmented range and ongoing habitat degradation. Threats to the species include habitat loss, increased human presence near the streams it inhabits, and possibly nitrate pollution caused by fertiliser overuse. (Full article...) -
Image 6Kahaani (IPA: [kəˈɦaːni]; transl. Story) is a 2012 Indian Hindi-language thriller film co-written, co-produced, and directed by Sujoy Ghosh. It stars Vidya Balan as Vidya Bagchi, a pregnant woman looking for her missing husband in Kolkata during the festival of Durga Puja, assisted by Assist Sub-Inspector Satyoki "Rana" Sinha (Parambrata Chatterjee) and Inspector General A. Khan (Nawazuddin Siddiqui).
Made on a shoestring budget of ₹80 million (US$960,000), Kahaani was conceived and developed by Ghosh, who co-wrote the film with Advaita Kala. The crew often employed guerrilla-filmmaking techniques on Kolkata's city streets to avoid attracting attention. Its creative portrayal of the city and its use of local crew and cast members made it a notable film. Kahaani explores themes of feminism and motherhood in a male-dominated Indian society. The film also makes several allusions to Satyajit Ray's films, such as Charulata (1964), Aranyer Din Ratri (1970), and Joi Baba Felunath (1979). The film's musical score and soundtrack are composed by Clinton Cerejo and Vishal–Shekhar respectively, with cinematography handled by Setu and editing done by Namrata Rao. (Full article...) -
Image 7Taare Zameen Par (lit. 'Stars on Earth'), also known as Like Stars on Earth in English, is a 2007 Indian Hindi-language psychological drama film produced and directed by Aamir Khan. It stars Khan himself, with Darsheel Safary, Tanay Chheda, Vipin Sharma and Tisca Chopra. It explores the life and imagination of Ishaan (Safary), an artistically gifted 8-year-old boy whose poor academic performance leads his parents to send him to a boarding school, where a new art teacher Nikumbh (Khan) suspects that he is dyslexic and helps him to overcome his reading disorder.
Creative director and writer Amole Gupte developed the idea with his wife Deepa Bhatia, who was the film's editor. Shankar–Ehsaan–Loy composed the score, and Prasoon Joshi wrote the lyrics for many of the songs. Principal photography took place in Mumbai, and in Panchgani's New Era High School, where some of the school's students participated in the filming. (Full article...) -
Image 8The frontispiece of the 1920 edition of Tod's Annals and Antiquities of Rajast'han
Lieutenant-Colonel James Tod (20 March 1782 – 18 November 1835) was an officer of the British East India Company and an Oriental scholar. He combined his official role and his amateur interests to create a series of works about the history and geography of India, and in particular the area then known as Rajputana that corresponds to the present day state of Rajasthan, and which Tod referred to as Rajast'han.
Tod was born in London and educated in Scotland. He joined the East India Company as a military officer and travelled to India in 1799 as a cadet in the Bengal Army. He rose quickly in rank, eventually becoming captain of an escort for an envoy in a Sindian royal court. After the Third Anglo-Maratha War, during which Tod was involved in the intelligence department, he was appointed Political Agent for some areas of Rajputana. His task was to help unify the region under the control of the East India Company. During this period Tod conducted most of the research that he would later publish. Tod was initially successful in his official role, but his methods were questioned by other members of the East India Company. Over time, his work was restricted and his areas of oversight were significantly curtailed. In 1823, owing to declining health and reputation, Tod resigned his post as Political Agent and returned to England. (Full article...) -
Image 9Parinda (transl. Bird) is a 1989 Indian Hindi-language crime drama film directed, produced and distributed by Vidhu Vinod Chopra. The film stars Jackie Shroff, Anil Kapoor, Nana Patekar and Madhuri Dixit. The story and scenario were written by Chopra, while Shiv Kumar Subramaniam and Imtiyaz Husain wrote the screenplay and dialogues, respectively. R. D. Burman composed the music and Khurshid Hallauri wrote the lyrics. Binod Pradhan served as the film's cinematographer and Renu Saluja was its editor.
Parinda follows Kishan (Shroff), who works for the underworld chieftain Anna (Patekar). Kishan's brother Karan (Kapoor) returns home after completing his studies in the United States. The two brothers are caught on different sides of a gang war after Karan decides to avenge his friend's death by Anna. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Typhoon Gay, also known as the Kavali Cyclone of 1989, was a small but powerful tropical cyclone which caused more than 800 fatalities in and around the Gulf of Thailand in November 1989. The worst typhoon to affect the Malay Peninsula in thirty-five years, Gay originated from a monsoon trough over the Gulf of Thailand in early November. Owing to favorable atmospheric conditions, the storm rapidly intensified, attaining winds over 120 km/h (75 mph) by 3 November. Later that day, Gay became the first typhoon since 1891 to make landfall in Thailand, striking Chumphon Province with winds of 185 km/h (115 mph). The small storm emerged into the Bay of Bengal and gradually reorganized over the following days as it approached southeastern India. On 8 November, Gay attained its peak intensity as a Category 5-equivalent cyclone with winds of 260 km/h (160 mph). The cyclone then moved ashore near Kavali, Andhra Pradesh. Rapid weakening ensued inland, and Gay dissipated over Maharashtra early on 10 November.
The typhoon's rapid development took hundreds of vessels by surprise, leading to 275 offshore fatalities. Of these, 91 occurred after an oil drilling ship, the Seacrest, capsized amid 6–11 m (20–36 ft) swells. Across the Malay Peninsula, 588 people died from various storm-related incidents. Several towns in coastal Chumphon were destroyed. Losses throughout Thailand totaled ฿11 billion (US $497 million). Striking India as a powerful cyclone, Gay damaged or destroyed about 20,000 homes in Andhra Pradesh, leaving 100,000 people homeless. In that country, 69 deaths and ₹410 million (US $25.3 million) in damage were attributed to Gay. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Reginald Heber (21 April 1783 – 3 April 1826) was an English Anglican bishop, a man of letters, and hymn-writer. After 16 years as a country parson, he served as Bishop of Calcutta until his death at the age of 42. The son of a rich landowner and cleric, Heber gained fame at the University of Oxford as a poet. After graduation he made an extended tour of Scandinavia, Russia and Central Europe. Ordained in 1807, he took over his father's old parish, Hodnet, Shropshire. He also wrote hymns and general literature, including a study of the works of the 17th-century cleric Jeremy Taylor.
He was consecrated Bishop of Calcutta in October 1823. He travelled widely and worked to improve the spiritual and general living conditions of his flock. Arduous duties, a hostile climate and poor health led to his collapse and death after less than three years in India. Memorials were erected there and in St Paul's Cathedral, London. A collection of his hymns appeared soon after his death. "Holy, Holy, Holy! Lord God Almighty" remains popular for Trinity Sunday, while "Brightest and Best" is frequently sung during Epiphany. (Full article...) -
Image 12Dilwale Dulhania Le Jayenge (transl. The Brave-Hearted Will Take the Bride), also known by the initialism DDLJ, is a 1995 Indian Hindi-language musical romance film written and directed by Aditya Chopra in his directorial debut and produced by his father Yash Chopra. Released on 20 October 1995, the film stars Shah Rukh Khan and Kajol as Raj and Simran, two young non-resident Indians, who fall in love during a vacation through Europe with their friends. Raj tries to win over Simran's family so the couple can marry, but Simran's father has long since promised her hand to his friend's son. The film was shot in India, London, and Switzerland, from September 1994 to August 1995.
With an estimated total gross of ₹102.5 crore (today's adjusted gross ₹524 crore), with ₹89 crore (today's adjusted gross ₹455 crore) earned in India and ₹13.50 crore (today's adjusted gross ₹69 crore) in overseas, the film was the highest-grossing Indian film of 1995 and one of the most successful Indian films in history. When adjusted for inflation, it is the second highest-grossing Indian film of the 1990s, behind Hum Aapke Hain Koun..! It won 10 Filmfare Awards—the most for a single film at that time—and the National Film Award for Best Popular Film Providing Wholesome Entertainment. Its soundtrack album became one of the most popular of the 1990s. (Full article...) -
Image 13

Profile of a Hoysala temple at Somanathapura
Hoysala architecture is the building style in Hindu temple architecture developed under the rule of the Hoysala Empire between the 11th and 14th centuries, in the region known today as Karnataka, a state of India. Hoysala influence was at its peak in the 13th century, when it dominated the Southern Deccan Plateau region. Large and small temples built during this era remain as examples of the Hoysala architectural style, including the Chennakesava Temple at Belur, the Hoysaleswara Temple at Halebidu, and the Kesava Temple at Somanathapura. These three temples were accorded UNESCO world heritage site status in 2023. Other examples of Hoysala craftsmanship are the temples at Belavadi, Amruthapura, Hosaholalu, Mosale, Arasikere, Basaralu, Kikkeri and Nuggehalli. Study of the Hoysala architectural style has revealed a negligible Indo-Aryan influence while the impact of Southern Indian style is more distinct.
Temples built prior to Hoysala independence in the mid-12th century reflect significant Western Chalukya influences, while later temples retain some features salient to Western Chalukya architecture but have additional inventive decoration and ornamentation, features unique to Hoysala artisans. Some three hundred temples are known to survive in present-day Karnataka state and many more are mentioned in inscriptions, though only about seventy have been documented. The greatest concentration of these are in the Malnad (hill) districts, the native home of the Hoysala kings. (Full article...) -
Image 14Portrait by Alexander Bassano, 1882
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days—which was longer than those of any of her predecessors—constituted the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India.
Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 after her father's three elder brothers died without surviving legitimate issue. Victoria, a constitutional monarch, attempted privately to influence government policy and ministerial appointments; publicly, she became a national icon who was identified with strict standards of personal morality. (Full article...) -
Image 15
INS Vikrant (from Sanskrit vikrānta, "courageous") was a Majestic-class aircraft carrier of the Indian Navy. The ship was laid down as HMS Hercules for the British Royal Navy during World War II, but was put on hold when the war ended. India purchased the incomplete carrier in 1957, and construction was completed in 1961. Vikrant was commissioned as the first aircraft carrier of the Indian Navy and played a key role in enforcing the naval blockade of East Pakistan during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971.
In its later years, the ship underwent major refits to embark modern aircraft, before being decommissioned in January 1997. She was preserved as a museum ship in Naval Docks, Mumbai until 2012. In January 2014, the ship was sold through an online auction and scrapped in November 2014 after final clearance from the Supreme Court. (Full article...) -
Image 16Chandralekha (also spelt Chandraleka) is a 1948 Indian historical adventure film produced and directed by S. S. Vasan of Gemini Studios. Starring T. R. Rajakumari, M. K. Radha and Ranjan, the film follows two brothers (Veerasimhan and Sasankan) who fight over ruling their father's kingdom and marrying a village dancer, Chandralekha.
Development began during the early 1940s when, after two successive box-office hits, Vasan announced that his next film would be entitled Chandralekha. However, when he launched an advertising campaign for the film he only had the name of the heroine from a storyline he had rejected. Veppathur Kittoo (one of Vasan's storyboard artists) developed a story based on a chapter of George W. M. Reynolds' novel, Robert Macaire: or, The French bandit in England. Original director T. G. Raghavachari left the film more than halfway through because of disagreements with Vasan, who took over in his directorial debut. (Full article...) -
Image 17
Preity G Zinta (pronounced [ˈpriːt̪i ˈzɪɳʈa]; born 31 January 1975) is an Indian actress and entrepreneur primarily known for her work in Hindi films. After graduating with degrees in English honours and criminal psychology, Zinta made her acting debut in Dil Se.. in 1998, followed by a role in Soldier in the same year. These performances earned her the Filmfare Award for Best Female Debut, and she was later recognised for her role as a teenage single mother in Kya Kehna (2000). She established a career as a leading Hindi film actress of the decade with a variety of character types. Her roles, often deemed culturally defiant, along with her unconventional screen persona won her recognition and several accolades.
Following critically appreciated roles in Chori Chori Chupke Chupke (2001), Dil Chahta Hai (2001), Dil Hai Tumhaara (2002), and Armaan (2003), Zinta received the Filmfare Award for Best Actress for her performance in Kal Ho Naa Ho (2003). She starred in two consecutive annual top-grossing films in India, Koi... Mil Gaya (2003) and Veer-Zaara (2004), and was noted for her portrayal of independent, modern Indian women in Salaam Namaste (2005) and Kabhi Alvida Naa Kehna (2006), top-grossing productions in domestic and overseas markets. For her first international role in the Canadian drama Heaven on Earth (2008) she was awarded the Silver Hugo Award for Best Actress and nominated for the Genie Award for Best Actress. She followed this with a hiatus from acting work for several years, with intermittent appearances such as in her self-produced comeback film, Ishkq in Paris (2013), which failed to leave a mark. (Full article...) -
Image 18Rashtrakuta control around 790 AD, during the Tripartite Struggle
The Rashtrakutas were a royal Indian dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the 6th and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing their rule from Manapur, a city in Central or West India. Other ruling Rashtrakuta clans from the same period mentioned in inscriptions were the kings of Achalapur and the rulers of Kannauj. Several controversies exist regarding the origin of these early Rashtrakutas, their native homeland and their language.
The Elichpur clan was a feudatory of the Badami Chalukyas, and during the rule of Dantidurga, it overthrew Chalukya Kirtivarman II and went on to build an empire with the Gulbarga region in modern Karnataka as its base. This clan came to be known as the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta, rising to power in South India in 753 AD. At the same time the Pala dynasty of Bengal and the Prathihara dynasty of Gurjaratra were gaining force in eastern and northwestern India respectively. An Arabic text, Silsilat al-Tawarikh (851), called the Rashtrakutas one of the four principal empires of the world. (Full article...) -
Image 19

Monier Williams, elected as the second Boden Professor of Sanskrit in 1860; this photograph was taken by Lewis Carroll.
The election in 1860 for the position of Boden Professor of Sanskrit at the University of Oxford was a competition between two candidates offering different approaches to Sanskrit scholarship. One was Monier Williams, an Oxford-educated Englishman who had spent 14 years teaching Sanskrit to those preparing to work in British India for the East India Company. The other, Max Müller, was a German-born lecturer at Oxford specialising in comparative philology, the science of language. He had spent many years working on an edition of the Rig Veda (an ancient collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns) and had gained an international reputation for his scholarship. Williams, in contrast, worked on later material and had little time for the "continental" school of Sanskrit scholarship that Müller exemplified. Williams regarded the study of Sanskrit as a means to an end, namely the conversion of India to Christianity. In Müller's opinion, his own work, while it would assist missionaries, was also valuable as an end in itself.
The election came at a time of public debate about Britain's role in India in the wake of the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Opinions were divided on whether greater efforts should be made to convert India or whether to remain sensitive to local culture and traditions. Both men battled for the votes of the electorate (the Convocation of the university, consisting of over 3,700 graduates) through manifestos and newspaper correspondence. Williams laid great stress in his campaign on the intention of the original founder of the chair, that the holder should assist in converting India through dissemination of the Christian scriptures. Müller's view was that his work on the Rig Veda was of great value for missionary work, and published testimonials accordingly. He also wanted to teach wider subjects such as Indian history and literature to assist missionaries, scholars, and civil servants – a proposal that Williams criticised as not in accordance with the original benefactor's wishes. The rival campaigns took out newspaper advertisements and circulated manifestos, and different newspapers backed each man. Although generally regarded as superior to Williams in scholarship, Müller had the double disadvantage (in the eyes of some) of being German and having liberal Christian views. Some of the newspaper pronouncements in favour of Williams were based on a claimed national interest of having an Englishman as Boden professor to assist with the work of governing and converting India. (Full article...) -
Image 20
Freida Selena Pinto (born 18 October 1984) is an Indian actress who has appeared mainly in American and British films. Born and raised in Mumbai, Maharashtra, she resolved at a young age to become an actress. As a student at St. Xavier's College, Mumbai she took part in amateur plays. After graduation, she briefly worked as a model and then as a television presenter.
Pinto rose to prominence with her film debut in the drama Slumdog Millionaire (2008), winning a SAG Award and earning a nomination for the BAFTA Award for Best Supporting Actress. She earned critical acclaim for her roles in Miral (2010), Trishna (2011), and Desert Dancer (2014).She also saw commercial success with the science fiction film Rise of the Planet of the Apes (2011), and the epic fantasy action film Immortals (2011). Pinto's other notable roles include You Will Meet a Tall Dark Stranger (2010), Love Sonia (2018), Hillbilly Elegy (2020), and Mr. Malcolm's List (2022). She also starred in the Showtime miniseries Guerrilla (2017), and had a recurring role in the Hulu series The Path (2018). (Full article...) -
Image 21Kal Ho Naa Ho (transl. Tomorrow may never come, pronounced [kəl ɦoː naː ɦoː]), also abbreviated as KHNH, is a 2003 Indian Hindi-language romantic comedy drama film directed by Nikhil Advani in his directorial debut with a story written by Karan Johar with dialogue by Niranjan Iyengar, and produced by Yash Johar. The film stars Jaya Bachchan, Shah Rukh Khan, Saif Ali Khan, and Preity Zinta, with Sushma Seth, Reema Lagoo, Lillete Dubey, and Delnaaz Irani in supporting roles. In the film, Naina Catherine Kapur (Zinta) and Aman Mathur (Shah Rukh Khan) fall in love, but a secret prevents him from reciprocating his feelings and results in a plan to set Naina up with her best friend, Rohit Patel (Saif Ali Khan).
Collaborating with Johar, Shankar–Ehsaan–Loy composed the soundtrack and score. Anil Mehta, Manish Malhotra, and Sharmishta Roy were the cinematographer, costume designer and art director, respectively. Principal photography took place in Toronto, New York City, and Mumbai from January to October 2003. The soundtrack was released on 27 September 2003 to positive reviews; the title song, "It's The Time To Disco", "Kuch To Hua Hai", and "Pretty Woman" were particularly well-received. (Full article...) -
Image 22
Kaikhosru Shapurji Sorabji (born Leon Dudley Sorabji; 14 August 1892 – 15 October 1988) was an English composer, music critic, pianist and writer whose music, written over a period of seventy years, ranges from sets of miniatures to works lasting several hours. One of the most prolific 20th-century composers, he is best known for his piano pieces, notably nocturnes such as Gulistān and Villa Tasca, and large-scale, technically intricate compositions, which include seven symphonies for piano solo, four toccatas, Sequentia cyclica and 100 Transcendental Studies. He felt alienated from English society by reason of his homosexuality and mixed ancestry, and had a lifelong tendency to seclusion.
Sorabji was educated privately. His mother was English and his father a Parsi businessman and industrialist from India, who set up a trust fund that freed his family from the need to work. Although Sorabji was a reluctant performer and not a virtuoso, he played some of his music publicly between 1920 and 1936. In the late 1930s, his attitude shifted and he imposed restrictions on performance of his works, which he lifted in 1976. His compositions received little exposure in those years and he remained in public view mainly through his writings, which include the books Around Music and Mi contra fa: The Immoralisings of a Machiavellian Musician. During this time, he also left London and eventually settled in the village of Corfe Castle, Dorset. Information on Sorabji's life, especially his later years, is scarce, with most of it coming from the letters he exchanged with his friends. (Full article...) -
Image 23

Map 1: Mysore and Coorg in a map of peninsular India showing shifting boundaries
The political history of the region on the Deccan Plateau in west-central peninsular India (Map 1) that was later divided into Mysore state and Coorg province saw many changes after the fall of the Hindu Vijayanagara Empire in 1565. The rise of Sultan Haidar Ali in 1761 introduced a new period.
At the height of the Vijayanagara Empire, the Mysore and Coorg region was ruled by diverse chieftains, or rajas ("little kings"). Each raja had the right to govern a small region, but also an obligation to supply soldiers and annual tribute for the empire's needs. After the empire's fall and the subsequent eastward move of the diminished ruling family, many chieftains tried to loosen their imperial bonds and expand their realms. Sensing opportunity amidst the new uncertainty, various powers from the north invaded the region. Among these were the Sultanate of Bijapur to the northwest, the Sultanate of Golconda to the northeast, the newly-formed Maratha empire farther northwest, and the major contemporary empire of India, the Mughal, which bounded all on the north. For much of the 17th century the tussles between the little kings and the big powers, and amongst the little kings, culminated in shifting sovereignties, loyalties, and borders. By the turn of the 18th century, the political landscape had become better defined: the northwestern hills were being ruled by the Nayaka rulers of Ikkeri, the southwestern—in the Western Ghats—by the Rajas of Coorg, the southern plains by the Wodeyar rulers of Mysore, all of which were Hindu dynasties; and the eastern and northeastern regions by the Muslim Nawabs of Arcot and Sira. Of these, Ikkeri and Coorg were independent, Mysore, although much-expanded, was formally a Mughal dependency, and Arcot and Sira, Mughal subahs (or provinces). (Full article...) -
Image 24
Prince Sadruddin Aga Khan (17 January 1933 – 12 May 2003) was a French-born statesman and activist who served as United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees from 1966 to 1977, during which he reoriented the agency's focus beyond Europe and prepared it for an explosion of complex refugee issues. He was also a proponent of greater collaboration between non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and UN agencies. The Prince's interest in ecological issues led him to establish the Bellerive Foundation in the late 1970s, and he was a knowledgeable and respected collector of Islamic art.
Born in Paris, France, he was the son of Sir Sultan Mahomed Shah Aga Khan and Princess Andrée Aga Khan. He married twice, but had no children of his own. Prince Sadruddin died of cancer at the age of 70, and was buried in Switzerland. (Full article...) -
Image 25
Western Ganga was an important ruling dynasty of ancient Karnataka in India which lasted from about 350 to 999 CE. They are known as "Western Gangas" to distinguish them from the Eastern Gangas who in later centuries ruled over Kalinga (modern Odisha and Northern Andhra Pradesh). The general belief is that the Western Gangas began their rule during a time when multiple native clans asserted their freedom due to the weakening of the Pallava empire in South India, a geo-political event sometimes attributed to the southern conquests of Samudra Gupta. The Western Ganga sovereignty lasted from about 350 to 550 CE, initially ruling from Kolar and later, moving their capital to Talakadu on the banks of the Kaveri River in modern Mysore district.
After the rise of the imperial Chalukyas of Badami, the Gangas accepted Chalukya overlordship and fought for the cause of their overlords against the Pallavas of Kanchi. The Chalukyas were replaced by the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta in 753 CE as the dominant power in the Deccan. After a century of struggle for autonomy, the Western Gangas finally accepted Rashtrakuta overlordship and successfully fought alongside them against their foes, the Chola Dynasty of Tanjavur. In the late 10th century, north of Tungabhadra river, the Rashtrakutas were replaced by the emerging Western Chalukya Empire and the Chola Dynasty saw renewed power south of the Kaveri river. The defeat of the Western Gangas by Cholas around 1000 resulted in the end of the Ganga influence over the region. (Full article...)
Selected pictures
-
Image 1A statue of the Hindu god Shiva as Nataraja, the Lord of Dance. In this form, Shiva performs his divine dance to destroy a weary universe and make preparations for the god Brahma to start the process of creation. A Telugu and Tamil concept, Shiva was first depicted as Nataraja in the famous Chola bronzes and sculptures of Chidambaram. The form is present in most Shiva temples in South India, and is the main deity in Chidambaram Temple, the foremost Shaivist temple.
-
Image 2Photograph: Yann; edit: Jim CarterA view of the Taj Mahal from the south, featuring the Charbagh garden. The mausoleum complex also includes subsidiary tombs, waterworks infrastructure, the small town of Taj Ganji, and a "moonlight garden". Its origins and architecture have been extensively documented, covering both the circumstances of its commission and the cultural and historical influence of the Islamic Mughal Empire in India.
-
Image 3Photograph: Muhammad Mahdi KarimAn Indian palm squirrel (Funambulus palmarum) photographed in Bangalore, India. In India these squirrels are associated with the Hindu deity Rama, an avatar of Vishnu, and as such are not to be harmed. However, in Western Australia they are considered pests and at times targeted for eradication.
-
Image 4Image credit: Vaikunda RajaThe Lotus-Namam is the symbol of Ayyavazhi, a Dharmic belief system that originated in South India in the 19th century. The lotus represents the 1,008-petalled Sahasrara and the flame-shaped white Namam represents the Aanma Jyothi or ātman, sometimes translated as 'soul' or 'self'. The number of practitioners is estimated to be between 700,000 and 8,000,000, although the exact number is unknown, since Ayyavazhis are reported as Hindus during censuses.
-
Image 5Photograph: Muhammad Mahdi KarimA panoramic view of Bangalore from Corporation Circle, with UB City to the left and Richmond area to the right. Kanteerava Indoor Stadium is in the foreground. The third largest city in India, the city is known as the Silicon Valley of India for its numerous IT exports.
-
Image 6
 Coin design credit: East India Company and the Calcutta Mint; photographed by Andrew ShivaThe mohur is a gold coin that was formerly minted by several governments, including those of British India. It was usually equivalent in value to fifteen silver rupees. Gold mohurs issued by the British East India Company or the Crown are valuable collectors' items, and sell in auctions for high prices. The double mohur (minted between 1835 and 1918), with a value of thirty rupees, is the highest-denomination circulating coin ever issued in India. The 1835 two-mohur coin above was minted in the reign of King William IV, while the 1862 one-mohur coin below was minted in the reign of Queen Victoria; both are now part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History.
Coin design credit: East India Company and the Calcutta Mint; photographed by Andrew ShivaThe mohur is a gold coin that was formerly minted by several governments, including those of British India. It was usually equivalent in value to fifteen silver rupees. Gold mohurs issued by the British East India Company or the Crown are valuable collectors' items, and sell in auctions for high prices. The double mohur (minted between 1835 and 1918), with a value of thirty rupees, is the highest-denomination circulating coin ever issued in India. The 1835 two-mohur coin above was minted in the reign of King William IV, while the 1862 one-mohur coin below was minted in the reign of Queen Victoria; both are now part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History. -
Image 7Photograph: Muhammad Mahdi KarimThe Bara Imambara is an imambara complex in Lucknow, India. Built by Asaf-ud-Daula, Nawab of Awadh, in 1785, the building reflects a maturation of ornamented Mughal design (as seen in the Badshahi Mosque).
-
Image 8Photograph credit: Jeevan JoseLeptosia nina, known as the psyche, is a species of butterfly in the family Pieridae (the sulphurs, yellows and whites), found in the Indian subcontinent, southeastern Asia, and Australia. It has a small wingspan of 2.5 to 5 cm (1 to 2 in). The upper side of the otherwise white forewing has a large, somewhat pear-shaped, black spot; this spot is also present on the underside which is scattered with greenish dots and speckles, sometimes arranged in bands. This L. nina butterfly was photographed in Kerala, India.
-
Image 9Photograph credit: Charles James SharpDanaus genutia, the common tiger or striped tiger, is a species of brush-footed butterfly found in Sri Lanka, India, Myanmar, south-eastern Asia and Australia. It prefers areas of moderate to heavy rainfall, and typical habitats include scrubby jungle, deciduous forests and fallow land near habitations. The insect sequesters toxins from plants, and advertises its unpalatability by having prominent markings and striking colour patterns. This adult male common tiger, of the subspecies D. g. genutia, was photographed in Kerala, India.
-
Image 10Photograph credit: Charles J. SharpThe nilgai or blue bull (Boselaphus tragocamelus) is the largest Asian antelope and is endemic to the Indian subcontinent. The sole member of the genus Boselaphus, the species was described and given its binomial name by German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. The nilgai stands 1–1.5 metres (3.3–4.9 ft) at the shoulder; males weigh 109–288 kilograms (240–635 lb), and the lighter females 100–213 kilograms (220–470 lb). A sturdy thin-legged antelope, the nilgai is characterised by a sloping back, a deep neck with a white patch on the throat, a short crest of hair along the neck terminating in a tuft, and white facial spots. A column of pendant coarse hair hangs from the dewlap ridge below the white patch. Sexual dimorphism is prominent – while females and juveniles are orange to tawny, adult males have a bluish-grey coat. Only males possess horns, which are 15–24 centimetres (5.9–9.4 in) in length.
This picture shows a male nilgai in a potato field at Jamtra, in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. -
Image 11Photograph: Augustus BinuChandiroor Divakaran (b. 1946) is a Malayalam–language poet and folk song writer from Kerala, India. He has published numerous collections of poetry since his debut collection, Radha, in 1965.
-
Image 12Map credit: PlaneMadA map of Network of National Highways in India, including NHDP projects up to phase IIIB, which is due to be completed by December 2012. The National Highways are the main long-distance roadways and constitute a total of about 58,000 km (36,250 mi), of which 4,885 km (3,053 mi) are central-separated expressways. Highways in India are around 2% of the total road network in India, but carry nearly 40% of the total road traffic.
-
Image 13Photograph: Augustus BinuArundhati Roy (b. 1961) is an Indian author and political activist who won the 1997 Man Booker Prize with her debut novel The God of Small Things. Born in Shillong, Meghalaya, Roy wrote several screenplays in the late 1980s after meeting (and later marrying) director Pradip Krishen. She wrote The God of Small Things over a four-year period ending in 1996; it was published the following year and received positive international reviews, although in India the work was controversial. She has continued to write essays and articles, but has yet to publish another novel.
-
Image 14Bangalore Town Hall is a neoclassical municipal building in Bangalore, India. It is sometimes known, after a former president of Bangalore, as the Sir K. P. Puttanna Chetty Town Hall. Built by Mirza Ismail in 1935, it underwent renovations in 1990 at a cost of ₹6.5 million (US$371,400 at the time).
-
Image 15Photograph credit: Bourne & Shepherd; retouched by Yann ForgetThe Rudra Mahalaya Temple is an ancient temple complex at Siddhpur in the Patan district of Gujarat, India. The temple was completed in 1140 by Jayasimha Siddharaja, but in 1296, Alauddin Khalji sent an army under Ulugh Khan and Nusrat Khan, who dismantled the structure. In 1414 or 1415, the temple was further destroyed and the western part was converted into a congregational mosque by Muslim ruler Ahmad Shah I of the Muzaffarid dynasty. Apart from the mosque, the surviving fragments consist of two porches, a torana (ornamental gateway) and a few pillars.
 Featured list – show another
Featured list – show another
-
Image 1

Rajinikanth at the audio release of Enthiran (2010)
Rajinikanth is an Indian actor, film producer, screenwriter and also a playback singer who has appeared predominantly in Tamil cinema. He began his film career by playing antagonistic and supporting roles before graduating to a lead actor. After starring in numerous commercially successful films throughout the 1980s and 1990s, he has continued to hold a matinée idol status in the popular culture of Tamil Nadu. Writing for Slate, Grady Hendrix called him the "biggest movie star you've probably never heard of." Rajinikanth has also worked in other Indian film industries such as Hindi, Telugu, Kannada and Malayalam.
He made his cinematic debut with K. Balachander's 1975 Tamil drama Apoorva Raagangal, in which he played a minor role of an abusive husband. He had his first major role in Balachander's Telugu drama film Anthuleni Katha (1976), and got his breakthrough in Tamil with Moondru Mudichu (1976)—also directed by Balachander. His style and mannerisms in the latter earned recognition from the audience. In 1977, he acted in 15 films, playing negative characters in most of them, including Avargal, 16 Vayathinile, Aadu Puli Attam and Gaayathri. He had positive roles in Kavikkuyil, the Kannada film Sahodarara Savaal, and the Telugu film Chilakamma Cheppindi, in which he played the protagonist for the first time in his career. His role as a failed lover in S. P. Muthuraman's Bhuvana Oru Kelvi Kuri (1977) won him critical acclaim. In 1978, he was cast as the main lead in the Tamil film Bairavi. The same year, he received critical acclaim for his roles in Mullum Malarum and Aval Appadithan; the former earned him a Tamil Nadu State Film Award Special Prize for Best Actor. He made his Malayalam cinema debut with I. V. Sasi's fantasy Allauddinum Albhutha Vilakkum (1979), an adaptation of a story from One Thousand and One Nights. By the end of the decade, he had worked in all South Indian languages and established a career in Tamil cinema. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Khan in 2015
Irrfan Khan (7 January 1967– 29 April 2020) was an Indian actor who worked in Indian and British-American films. His on-screen debut was a minor role in Mira Nair's Salaam Bombay! in 1988. He followed this with appearances in a variety of television shows in the late 1980s to 1990s including playing ʽAbd al-Qadir Badayuni in Bharat Ek Khoj (1988), Makhdoom Mohiuddin in Kahkashan (1991), Vladimir Lenin in Lal Ghas Per Neele Ghodey (1992), a dual role in Chandrakanta (1994), and Valmiki in Jai Hanuman (1997). Khan found his television work unfulfilling and considered quitting acting.
His career experienced a turnaround with his breakthrough role as the lead in Asif Kapadia's The Warrior (2001), which won the BAFTA Award for Outstanding British Film. He followed this with critically acclaimed villainous roles in Haasil and Maqbool (both in 2003). For the former performance, where he played a devious politician, Khan received the Filmfare Award for Best Performance in a Negative Role. In 2006, Khan portrayed a first-generation Bengali immigrant in the Nair-directed film The Namesake with Tabu and a hitman in The Killer. The following year, he won the Filmfare Award for Best Supporting Actor for his performance as a 38-year-old man waiting to marry the right woman in Life in a... Metro, directed by Anurag Basu. In 2008, he received international recognition for his role as a police inspector in Danny Boyle's Slumdog Millionaire, which won the Academy Award for Best Picture. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) was awarded to 153 members of the British Indian Army and civilians under its command, from 1857 until independence in 1947. The Victoria Cross is a military decoration awarded for valour "in the face of the enemy" to members of armed forces of some Commonwealth countries and previous British Empire territories. It takes precedence over all other Orders, decorations and medals. It may be awarded to a person of any rank in any service and to civilians under military command. The VC is traditionally presented to the recipient by the British monarch during an investiture at Buckingham Palace, though in a large number of cases this was not possible and it was presented in the field by a prominent civil or military official. The VC was introduced in Great Britain on 29 January 1856 by Queen Victoria to reward acts of valour during the Crimean War.
Indian troops were not originally eligible for the VC, because since 1837 they had been eligible for the Indian Order of Merit—the oldest British gallantry award for general issue. When the VC was created, Indian troops were still controlled by the British East India Company, and did not come under Crown control until 1860. European officers and men serving with the East India Company were not eligible for the Indian Order of Merit; the VC was extended to cover them in October 1857. It was only at the end of the 19th century that calls for Indian troops to be awarded the VC intensified. Indian troops became eligible for the award in 1911. The first awards to Indian troops appeared in The London Gazette on 7 December 1914 to Darwan Singh Negi and Khudadad Khan, whose gallantry on 31 October 1914 was nearly a month earlier than Negi's gallantry on 24/25 November. Negi was presented with the VC by King George V two days earlier, on 5 December 1914, during a visit to troops in France. He is one of a small number of soldiers presented with his award before it appeared in the London Gazette. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Matondkar in 2010
Urmila Matondkar is an Indian actress known for her work in Hindi films. She has appeared in over 60 films. She has been praised by the critics for her acting and dancing skills. She made her screen debut as a child artist in B.R. Chopra's Karm (1977), and later appeared in Shekhar Kapur's critically acclaimed Masoom (1983). After making her debut as the heroine in 1989 Malayalam thriller Chanakyan, Urmila began a full-time acting career, with a leading role in the 1991 action Narsimha. She rose to prominence with Ram Gopal Varma's blockbuster Rangeela (1995). Her portrayal of an aspiring actress, Mili Joshi, opposite Aamir Khan received praise from critics, and garnered her first nomination for the Filmfare Award for Best Actress.
In 1997, Urmila received a nomination for Filmfare Award for Best Supporting Actress for her performance in the drama Judaai. The following year, she starred in the crime drama Satya, which has been cited as one of the greatest films of Indian cinema, for which she received another nomination for Best Actress. The same year, her dance performance in the item number "Chamma Chamma" from China Gate won her rave reviews. In 1999, she received praise for playing a psychopath in the thriller Kaun and a reserved girl in the romantic comedy Khoobsurat, a box office success. Her other four releases of the year including Jaanam Samjha Karo, and Hum Tum Pe Marte Hain were commercial failures. She played an obsessive lover in the 2001 romantic drama Pyaar Tune Kya Kiya, which earned her a nomination for the Filmfare Award for Best Performance in a Negative Role. (Full article...) -
Image 5The 2022 recipient: Neena Gupta
The National Film Award for Best Actress in a Supporting Role (known as National Film Award for Best Supporting Actress prior to 69th NFA) is an honour presented annually at India's National Film Awards ceremony by the National Film Development Corporation of India (NFDC), an organisation set up by the Indian Ministry of Information and Broadcasting. Since 1984, the award is given by a national panel appointed annually by the NFDC to an actress for the best performance in a supporting role within Indian cinema. It is presented by the President of India at a ceremony held in New Delhi. Since the 70th National Film Awards, the name was changed to "Best Actress in a Supporting Role".
The winner is given a "Rajat Kamal" (Silver Lotus) certificate and a cash prize of ₹2,00,000. Including ties and repeat winners, the NFDC has presented a total of 41 Best Supporting Actress awards to 35 different actresses. Although Indian cinema produces films in more than 20 languages, the performances of films that have won awards are of ten languages: Hindi (19 awards), Malayalam (7 awards), Bengali (4 awards), Tamil (4 awards), English (2 awards), Meitei (1 award), Marathi (1 award), Urdu (1 award), Haryanvi (1 award), Odia (1 award). (Full article...) -
Image 6
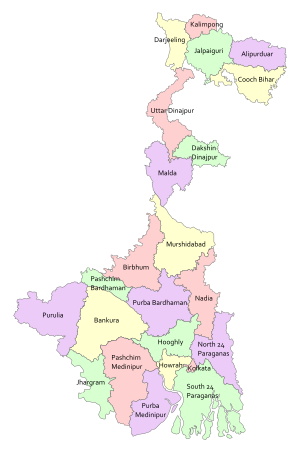
Districts of West Bengal
The Himalayas lies in the north of West Bengal and the Bay of Bengal is at the south. Between them, the river Ganga flows eastwards and its main distributary, the Hooghly River, flows south to reach the Bay of Bengal. The Siliguri Corridor, which connects North-East India with rest of the India, lies in the North Bengal region of the state. Geographically, West Bengal is divided into a variety of regions—Darjeeling Himalayan hill region, Terai and Dooars region, North Bengal plains, Rarh region, Western plateau and high lands, coastal plains, Sundarbans and the Ganga Delta.
In 1947, when India gained independence, the state of West Bengal was formed, with 14 districts, as per partition plan of the then Bengal province of British India. The former princely state Koch Bihar joined as a district on 26 January 1950, and the former French enclave Chandannagore joined as part of the Hooghly district in 1954. The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 led to addition of Purulia district to the state and to enlargement of West Dinajpur district. Later, larger districts such as West Dinajpur, 24 Parganas and Midnapore were bifurcated. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Rahul Dravid during the Australian tour of India in 2004
Rahul Dravid is a retired Indian international cricketer. in both Test and One Day International (ODI) cricket in matches organised by the International Cricket Council (ICC). Nicknamed "The Wall" for his ability of "... fending off the fiercest, the fastest and the wiliest of bowlers around the world", he scored 36 centuries (scores of 100 runs or more) in Test cricket and 12 in One Day Internationals (ODI) between his debut in 1996 and retirement in 2011. He was named as one of the five Wisden Cricketers of the Year in 2000, as well as the ICC Test Player of the Year and ICC Player of the Year in 2004.
Dravid scored his first Test century in January 1997 against South Africa. In a man-of-the-match performance, he made 148 runs spanning nine hours and took India to their only draw of the series. He made centuries in both innings of a match when he scored 190 and 103 not out in the final Test of the 1998–99 series against New Zealand. He repeated the feat in March 2005 when he scored 110 and 135 against Pakistan in another man-of-the-match performance, leading India to victory in the second of the three-match series. Scoring 180 in a fifth-wicket partnership of 376 with VVS Laxman, in the Second Test of the Border-Gavaskar Trophy in 2001, Dravid helped lead India to victory by 171 runs despite being asked to follow-on by the Australians. His partnership with Laxman was the third-highest for the fifth wicket in Test cricket history. Dravid's highest Test score of 270, achieved in April 2004 in Rawalpindi, helped India to an innings victory against Pakistan. The performance was the fourth-highest score by an Indian batsman in Test cricket. He scored centuries against all Test playing nations and was the first cricketer to score centuries in all 10 Test playing nations. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Tamannaah Bhatia is an Indian actress known for her work in Telugu, Tamil and Hindi cinema. She debuted as a leading lady in the Hindi film Chand Sa Roshan Chehra in 2005. That same year marked her Telugu debut with Sree, followed by her Tamil debut in Kedi the subsequent year. She experienced a breakthrough in her career with the success of Happy Days and Kalloori in 2007, portraying college students in both films. Her journey continued with box-office hits like Ayan, 100% Love, Siruthai, Tadakha, Oosaravelli, Racha and Veeram as well as setbacks such as Ananda Thandavam, Endukante Premanta, Himmatwala, Humshakals and Aagadu. Additionally, while she received critical acclaim and several accolades for her role in 100% Love, her performances in Himmatwala and Humshakals faced criticism.
In 2015, Bhatia received praised for her role in Baahubali: The Beginning, which earned over ₹600 crore. She was praised for her performances in Oopiri and Dharma Durai, and her double role in Devi was well received. However, Vasuvum Saravananum Onna Padichavanga, Bengal Tiger and Kaththi Sandai were less successful. In 2017, she reprised her role in Baahubali 2: The Conclusion, which grossed over ₹1700 crore worldwide, while Anbanavan Asaradhavan Adangadhavan was a box office failure. In 2018, Sketch received mixed reviews, but her performance was praised, while Naa Nuvve and Next Enti? were poorly received. In 2019, she starred in the blockbuster F2: Fun and Frustration and delivered notable performances in Kanne Kalaimaane, Devi 2, Khamoshi, Sye Raa Narasimha Reddy and Petromax. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Haasan in 2014
Shruti Haasan is an Indian actress and singer who works in Telugu, Hindi and Tamil films. She started her career as a playback singer at the age of six in the 1992 Tamil film Thevar Magan. She had a brief role in her father, Kamal Haasan's Tamil-Hindi directorial Hey Ram (2000) as a child artist. Haasan's first major appearance was in the Hindi film Luck (2009), in which she played a dual role of a woman avenging her twin sister's death. She played the female lead in the films Anaganaga O Dheerudu and 7aum Arivu; both were released in 2011 and together earned her the Best Female Debut – South at the 59th Filmfare Awards South ceremony.
Haasan's subsequent releases Oh My Friend (2011) and 3 (2012) were commercially unsuccessful. The latter earned her a nomination for the Best Actress – Tamil at the 60th Filmfare Awards South ceremony. A turning point came in Haasan's career with Harish Shankar's commercially successful Telugu film Gabbar Singh (2012). The release was followed by a series of successful films such as Balupu (2013) and Yevadu (2014). She received her first Filmfare Award for Best Actress – Telugu for her performance in Race Gurram (2014). (Full article...) -
Image 10The state president of the Indian National Congress is the state-level highest command of the Indian National Congress (INC), responsible for leading in political campaigns at state level. State presidents shoulder a diverse array of roles and responsibilities integral to the effective functioning of the party at the state-level. Also known as the leader of the state and union territory party, a state president is chosen by the party president.
Being the higher decision-making body, state presidents actively contribute to the formulation of state-level policies, representing the party's stance on relevant issues and engaging in the development and implementation of election strategies during state elections. In addition, a state president is tasked with overseeing the organizational structure of the Pradesh Congress Committee, including the appointment and coordination of leaders at various levels, such as the district committee, block committee, and each panchayat development block or panchayat samiti. Serving as a spokesperson for the party in the state, they communicate the party's positions to the media and keep party members informed about policies and decisions. State presidents also play a pivotal role in building and maintaining the party's membership, reaching out to diverse sections of society and addressing their concerns to advance the party's agenda. (Full article...) -
Image 11Satyajit Ray (listen; 2 May 1921 – 23 April 1992) was an Indian filmmaker who worked prominently in Bengali cinema. Ray received numerous awards and honours, including India's highest award in cinema, the Dadasaheb Phalke Award (1984) and India's highest civilian award, the Bharat Ratna (1992). He was also awarded the Commander of the National Order of the Legion of Honour, the highest decoration in France (1987) and an Honorary Award at the 64th Academy Awards (1991).
Often regarded as one of the greatest filmmakers of world cinema, Ray made his directorial debut in 1955 with Pather Panchali. The film earned critical acclaim and was awarded under the Best Film category at various award ceremonies and film festivals, including the 3rd National Film Awards (1955), 7th Berlin International Film Festival (1957), and 1st San Francisco International Film Festival (1957). Pather Panchali was also awarded the "Prix du document humain" prize at the 9th Cannes Film Festival (1956). Ray won thirty-five National Film Awards during his four-decade career. Six of his films—Pather Panchali, Apur Sansar (1959), Charulata (1964), Goopy Gyne Bagha Byne (1968), Seemabaddha (1971), and Agantuk (1991)—won the Best Feature Film. Three films—Jalsaghar (1958), Abhijan (1962), and Pratidwandi (1970)—were awarded with Second Best Feature Film and Mahanagar (1963) was adjudged the Third Best Feature Film. Ray's 1961 documentary on Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore received awards at the Locarno and Montevideo film festivals as well as the National Film Award for Best Non-Feature Film. His Hindi film Shatranj Ke Khilari (1977) won the National Film Award for Best Feature Film in Hindi, and the Filmfare Award for Best Director. Ray's Apu Trilogy (1955–59), comprising Pather Panchali, Aparajito (1956) and Apur Sansar (1959), appeared in Time's All-Time 100 Movies in 2005. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Dixit in 2019
Indian actress Madhuri Dixit made her acting debut in 1984 with Abodh where she portrayed a young bride. Dixit went on to appear in several films over the next three years, including the dramas Awara Baap (1985) and Swati (1986), though none of them garnered her much recognition. The role of Mohini in N. Chandra's action romance drama Tezaab (1988) proved to be a breakthrough for Dixit. The film went on to become the highest-grossing film of that year. For her performance, Dixit received a Best Actress nomination at Filmfare. She achieved further success by featuring as the female lead in several top-grossing action-dramas, including Ram Lakhan (1989), Tridev (1989), and Kishen Kanhaiya (1990). The role of a wealthy brat in the 1990 romantic drama Dil earned Dixit her first Filmfare Award for Best Actress. The following year, she starred in another box-office hit Saajan, and won a second Best Actress award at Filmfare for portraying the role of a strong woman who rebels against her manipulative mother-in-law in the 1992 drama Beta.
She featured alongside Jackie Shroff and Sanjay Dutt in the action thriller Khalnayak (1993), one of the highest-grossing films of that year. Subsequently, she played an avenger in the drama Anjaam (1994) to positive reviews. Dixit's subsequent release was Sooraj Barjatya's Hum Aapke Hain Koun..! (1994), a family drama which emerged as the highest-grossing Bollywood film to that point. The following year, she featured in Raja (1995) which was a blockbuster film of that year and Yaraana in which she played a woman who attempts an escape from her abusive husband. Both of her releases in 1996—Rajkumar and Prem Granth—were financial failures. Dixit's portrayal of a headstrong dancer in Yash Chopra's 1997 romance Dil To Pagal Hai was a major success, earning her a fourth Filmfare Award for Best Actress. She garnered critical acclaim for her work in the dramas Mrityudand (1997), Wajood (1998) and Pukar (2000). She portrayed five roles in the experimental film Gaja Gamini (2000). (Full article...) -
Image 13

Members of the Indian cricket team before a Women's World Twenty20 game in Sydney, 2009.
A women's Twenty20 International (WT20I) is a 20 overs-per-side cricket match played in a maximum of 150 minutes between two ICC member sides, and is played under the rules of Twenty20 cricket. The first such match was held in August 2004 between England and New Zealand. The India women's national cricket team played its first WT20I against England in August 2006; India won the match by eight wickets.
Since the team made its first WT20I appearance in 2006, 73 players—including five different captains—have represented India in the format. The list is arranged in the order in which each player won her first Twenty20 cap. Where more than one player won her first Twenty20 cap in the same match, those players are listed alphabetically by surname. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Sachin Tendulkar has scored more centuries in Test cricket than any other player.
Sachin Tendulkar is a retired Indian cricketer who is widely acknowledged as one of the greatest batsmen of all time, he is the most prolific run-scorer in international cricket. Tendulkar has scored the highest number of centuries (100 or more runs) in Test matches and One Day International (ODI) matches organised by the International Cricket Council. His total of 51 centuries in Test matches is a world record for highest number of centuries by a batsman and his 49 centuries in ODI matches are the second highest number of centuries after Virat Kohli. He became the first and only cricketer to score 100 international centuries when he made 114 against Bangladesh in March 2012.
After making his Test debut in 1989, Tendulkar achieved his first century against England at Old Trafford, Manchester in 1990; he made 119 not out. In Test matches, Tendulkar has scored centuries against all the Test cricket playing nations, and is the second batsman to score 150 against each of them. He has scored a century in at least one cricket ground of all Test cricket playing nations, except Zimbabwe. In October 2010, Tendulkar went past Brian Lara's record of 19 scores of 150 or more by hitting his 20th against Australia in Bangalore. He made his highest score in 2004, when he made 248 not out against Bangladesh at the Bangabandhu National Stadium, Dhaka. Tendulkar has scored six double centuries and remained unbeaten on 15 occasions. His centuries have come in 30 different cricket grounds, with 27 of them being scored in venues outside India. Tendulkar has been dismissed nine times between scores of 90 and 99. (Full article...) -
Image 15

Chopra at the 21st Lions Gold Awards where she won the Best Actress award for Mary Kom (2014)
Priyanka Chopra is an Indian actress who has received several awards and nominations including two National Film Award, five Filmfare Awards, eight Producers Guild Film Awards, eight Screen Awards, six IIFA Awards, and two People's Choice Awards. In 2000, she participated in the Femina Miss India contest, where she finished second, winning the Femina Miss India World title. She then entered the Miss World pageant and was crowned Miss World 2000, becoming the fifth Indian to win the contest. Chopra made her Bollywood film debut with a supporting role in the 2003 spy thriller The Hero, which earned her the Stardust Award for Best Supporting Actress. The same year, her performance in the romantic musical Andaaz won her the Filmfare Award for Best Female Debut and a nomination for Best Supporting Actress at the same ceremony. For her portrayal of a seductress in the romantic thriller Aitraaz, Chopra won the Filmfare Award for Best Performance in a Negative Role and received her second nomination for Best Supporting Actress. The same year, she was nominated for the IIFA Award for Best Actress for the romantic comedy Mujhse Shaadi Karogi.
Chopra starred as a troubled model in the drama Fashion (2008), for which she won many Best Actress awards in India including the National Film Award for Best Actress and the Filmfare Award in the same category. In 2010, she received several Best Actress nominations for playing a feisty Marathi woman in the caper thriller Kaminey, winning her second consecutive Producers Guild Film Award for Best Actress in a Leading Role after Fashion. The same year, she was nominated for the Screen Award for Best Actress for playing twelve distinct roles in the social comedy film What's Your Raashee?. For her portrayal of a serial killer, in the 2011 neo-noir 7 Khoon Maaf, she won the Filmfare Award for Best Actress (Critics), in addition to a Best Actress nomination at the same ceremony. (Full article...) -
Image 16Enthiran (transl. Robot) is a 2010 Indian Tamil-language science fiction film directed by S. Shankar and produced by Kalanithi Maran. Shankar wrote the screenplay and co-wrote the dialogues with Sujatha and Madhan Karky. The film stars Rajinikanth and Aishwarya Rai with Danny Denzongpa, Santhanam, and Karunas playing supporting roles. The musical score was composed by A. R. Rahman while the cinematography, visual effects, editing, and art direction were handled by R. Rathnavelu, V. Srinivas Mohan, Anthony, and Sabu Cyril respectively. The film's story revolves around a scientist's struggle to control his creation, an android robot whose software is upgraded to give it the ability to comprehend and generate human emotions. The plan backfires when the robot falls in love with the scientist's fiancée and is further manipulated by a rival scientist to bring destruction to all who stand in its way. The film was dubbed into Hindi as Robot.
Produced on an estimated budget of ₹1.32 billion, Enthiran was released on 1 October 2010 and yielded a revenue of ₹1.79 billion according to a report by the Sun TV Network. The film garnered awards and nominations in several categories, with particular praise for its cinematography, visual effects, art direction, costume design, and Rajinikanth's performance. The film has won 25 awards from 38 nominations. (Full article...) -
Image 17In cricket, a batsman reaches a triple century if they score 300 or more runs in a single innings. The Ranji Trophy is the premier first-class cricket championship played in India. Conducted by the Board of Control for Cricket in India, it was founded in 1934 as "The Cricket Championship of India". As of January 2020[update], a triple century has been scored on 46 occasions by 41 different batsmen in the Ranji Trophy.
The first triple century in the Ranji Trophy was scored by Maharashtra's Vijay Hazare against Baroda in the 1939–40 season. As of November January 2023[update], the most recent triple century in the tournament was scored by Prithvi Shaw from Mumbai, who made 379 against Assam in the 2022–23 season. The highest score in the competition was made by B. B. Nimbalkar, who scored 443 runs not out for Maharashtra against Kathiawar in the 1948–49 season. It is the only instance of a quadruple century in the tournament. The highest number of triple centuries are scored by Ravindra Jadeja, who has reached the milestone three times while playing for Saurashtra. Jadeja is followed by V. V. S. Laxman, Cheteshwar Pujara, and Wasim Jaffer, with two triple centuries each. Tamil Nadu's Woorkeri Raman and Arjan Kripal Singh are the only two batsmen to score triple centuries in the same innings. As of December 2016[update], five batsmen have scored 290–299 runs in an innings, and three of them were not out. (Full article...) -
Image 18

Vikram Vedha is a 2017 Indian Tamil-language neo-noir action thriller film directed and written by the husband and wife duo Pushkar–Gayathri and produced by S. Sashikanth under the banner of YNOT Studios. R. Madhavan and Vijay Sethupathi play the title characters Vikram and Vedha respectively. Shraddha Srinath, Kathir and Varalaxmi Sarathkumar play the other lead roles while Prem, Achyuth Kumar, Hareesh Peradi and Vivek Prasanna feature as supporting characters. Sam C. S. composed the film's soundtrack and score. Richard Kevin and P. S. Vinod was in charge of the editing and cinematography respectively.
A contemporary adaptation of the Indian folktale Baital Pachisi, the film follows Vikram, a police inspector who is decisive about good and evil, and the head of an encounter unit which is formed to track down and kill Vedha, a gangster. When the unit makes plans for another encounter, Vedha walks into the police station and voluntarily surrenders himself. He then tells Vikram three stories which bring about a change in the latter's perceptions of right and wrong. (Full article...) -
Image 19

Sheoo Mewalal, the first hat-trick scorer for India since independence
The first player ever to score a hat-trick (three or more goals in a match) for India in an international football match was R. Lumsden. He achieved the feat in an official friendly match against Australia on 24 September 1938, at the Sydney Showground, although India lost the match 4–5. This is the only instance when India have lost a game in which a player scored a hat-trick for the team. Lumsden was the only footballer to score a hat-trick for India before independence. Since independence in 1947, eleven Indian players have scored a hat-trick in an international football match. No Indian player has ever scored more than three goals in a single game. The first player after independence to score a hat-trick for India was Sheoo Mewalal in a 4–0 victory over Burma in the 1952 Colombo Quadrangular Tournament.
K. Appalaraju and Sunil Chhetri are the only Indian footballers to have scored a hat-trick more than once. Appalaraju achieved the feat twice in the two-legged tie against Ceylon during the 1964 Olympic Qualifiers. Chhetri has achieved the feat four times, the latest of which came in India's 4–0 victory over Pakistan in the opening match of the 2023 SAFF Championship. This is also the most recent instance of an Indian player scoring a hat-trick in an international football match. Chhetri's first hat-trick came in the final of the 2008 AFC Challenge Cup against Tajikistan, which helped India not only to win the cup but also to qualify directly for the AFC Asian Cup in 2011, the first time in 27 years that the team reached the final tournament. (Full article...) -
Image 20Shabana Azmi, Actress with a Record of Five in this Category
The National Film Award for Best Actress in a Leading Role is an honour presented annually at the National Film Awards of India since 1968 to an actress for the best performance in a leading role within the Indian film industry. The National Film Awards were called the "State Awards for Films" when established in 1954. The State Awards instituted the "Best Actress" category in 1968 as the "Urvashi Award for the Best Actress"; in 1975, the Urvashi Award was renamed as the "Rajat Kamal Award for the Best Actress". Throughout the years, accounting for ties and repeat winners, the Government of India has presented a total of 56 Best Actress awards to 45 different actresses. Since the 70th National Film Awards, the name was changed to "National Film Award for Best Actress in a Leading Role".
Until 1974, winners of the National Film Award received a figurine and certificate; since 1975, they have been awarded with a "Rajat Kamal" (silver lotus), certificate and a cash prize that amounted to ₹2 lakh (US$2,400) in the 70th edition. Although the Indian film industry produces films in more than 20 languages and dialects, the actresses whose performances have won awards have worked in eleven major languages: Hindi (22 awards),Tamil (8 awards), Bengali (7 awards), Malayalam (6 awards), Telugu (4 awards), Kannada (3 awards), English (3 awards), Marathi (2 awards), Assamese (one award),Gujarati (one award) and Urdu (one award). (Full article...) -
Image 21

The Wanderers Stadium, Johannesburg, where India played their first ever Twenty20 International
A Twenty20 International (T20I) is a form of cricket match between two representative teams, each having T20I status as determined by the International Cricket Council (ICC), and is played under the rules of Twenty20 cricket. The first such match was played between Australia and New Zealand on 17 February 2005. The Indian cricket team played its first T20I match—under the captaincy of Virender Sehwag—during the 2006–07 series in South Africa; India defeated the hosts by six wickets in the one-off match and claimed the series.
As of July 2024, 115 players have represented India in T20Is. India won the inaugural edition of the ICC World Twenty20, defeating Pakistan in the final by five runs. (Full article...) -
Image 22

The president of the Indian National Congress is the chief executive of the Indian National Congress (INC), one of the principal political parties in India. Constitutionally, the president is elected by an electoral college composed of members drawn from the Pradesh Congress Committees and members of the All India Congress Committee (AICC). In the event of any emergency because of any cause such as the death or resignation of the president elected as above, the most senior general secretary discharges the routine functions of the president until the Working Committee appoints a provisional president pending the election of a regular president by the AICC. The president of the party has effectively been the party's national leader, head of the party's organisation, head of the Working Committee, the chief spokesman, and all chief Congress committees.
After the party's foundation in December 1885, Womesh Chandra Banerjee became its first president. From 1885 to 1933, the presidency had a term of one year only. From 1933 onwards, there was no such fixed term for the president. During Jawaharlal Nehru's premiership, he rarely held the Presidency of INC, even though he was always head of the Parliamentary Party. Despite being a party with a structure, Congress under Indira Gandhi did not hold any organisational elections after 1978. In 1978, Gandhi split from the INC and formed a new opposition party, popularly called Congress (I), which the national election commission declared to be the real Indian National Congress for the 1980 general election. Gandhi institutionalised the practice of having the same person as the Congress president and the prime minister of India after the formation of Congress (I). Her successors Rajiv Gandhi and P. V. Narasimha Rao also continued that practice. Nonetheless, in 2004, when the Congress was voted back into power, Manmohan Singh became the first and only prime minister not to be the president of the party since establishment of the practice of the president holding both positions. (Full article...) -
Image 23In the Republic of India, a chief minister is the head of government of each of the twenty-eight states and three of the eight union territories. According to the Constitution of India, at the state level, the governor is de jure head, but de facto executive authority rests with the chief minister. Following elections to the state legislative assembly, the governor usually invites the party (or coalition) with a majority of seats to form the state government. The governor appoints the chief minister, whose council of ministers are collectively responsible to the assembly. Out of the thirty incumbents, except Tamil Nadu's M. K. Stalin, all other Chief Ministers also act as the leader of the house in their legislative assemblies. Given they have the assembly's confidence, the chief minister's term is usually for a maximum of five years; there are no limits to the number of terms they can serve.
Two of the incumbents are women — Mamata Banerjee in West Bengal,
who has the longest continuous incumbency serving since 20 March 2011 (for 13 years, 183 days) and Atishi Marlena in Delhi. Atishi (aged 43) is the also the youngest incumbent chief minister, while Kerala's Pinarayi Vijayan (aged 79) is the oldest. Nitish Kumar of Bihar has served for the most terms (nine). Thirteen incumbents belong to the Bharatiya Janata Party, three to the Indian National Congress, and two to the Aam Aadmi Party. No other party has more than one chief minister in office. (Full article...) -
Image 24India is a union consisting of 28 states and 8 union territories. As of 2022, with an estimated population of 1.4 billion, India is the world's most populous country. India occupies 2.4% of the world's area and is home to 17.5% of the world's population. The Indo-Gangetic Plain has one of the world's biggest stretches of fertile not-deep alluvium and are among the most densely populated areas of the world. The eastern and western coastal regions of Deccan Plateau are also densely populated regions of India. The Thar Desert in western Rajasthan is one of the most densely populated deserts in the world. The northern and north-eastern states along the Himalayas contain cold arid deserts with fertile valleys. These states have relatively low population density due to indomitable physical barriers. (Full article...)
-
Image 25

Kapil Dev is India's third highest wicket-taker in Test cricket.
Kapil Dev is a former Test and One Day International (ODI) cricketer who represented India between 1978 and 1994. He took 24 five-wicket hauls during his international career. In cricket, a five-wicket haul—also known as a five-for or fifer—refers to a bowler taking five or more wickets in a single innings. This is regarded as a notable achievement, and as of October 2024[update], only 54 bowlers have taken 15 or more five-wicket hauls at international level in their cricketing careers. A right-arm fast bowler, Kapil Dev took 434 wickets in Test cricket and 253 in ODIs. With 23 five-wicket hauls in Tests, he has the third highest number of international five-wicket hauls among Indian cricketers as of 2012, after Anil Kumble and Harbhajan Singh. Kapil Dev was named by the Wisden as one of their Cricketers of the Year in 1983 and Indian Cricketer of the Century in 2002. Eight years later, the International Cricket Council (ICC) inducted him into the ICC Cricket Hall of Fame. As of 2012, Kapil Dev also holds the record for being the only player to have taken more than 400 wickets and scored over 5,000 runs in Tests.
Kapil Dev made his Test and ODI debuts against Pakistan, both in 1978. His first five-wicket haul came a year later against England during the first Test of India's tour. His career-best bowling figures in an innings of nine for 83 was achieved in 1983 against the West Indies in Ahmedabad. In Tests, Kapil Dev was most successful against Pakistan and Australia, with seven five-wicket hauls against each of them. He took his only five-wicket haul in ODIs against Australia during the 1983 Cricket World Cup. (Full article...)
 Good article – show another
Good article – show another
-
Image 1Sridevi: The Eternal Screen Goddess is a biography by author and screenwriter Satyarth Nayak that chronicles the life and career of Indian actress Sridevi. Consisting of ten chapters, it describes her birth in 1963 in Egmore, her acting career in both the North and South Indian film industries, her marriage in 1996 to the film producer Boney Kapoor, with whom she has two daughters, and her death by accidental drowning in 2018. Published by Random House on 16 December 2019, the book was a success both commercially and critically, and reviewers commended it for the writing and comprehensiveness.
After authoring the mystery novel The Emperor's Riddles (2014) and scripting the historical television series Porus (2017–2018), Nayak wanted to experiment in writing a biography. 2017 was the year of Sridevi's 300th film, Mom; the news of the milestone aroused him to choose the actress as his next subject. Discussion of the book was started the same year, but writing started in mid-2018—following her death in February 2018—and was finished in around 1+1⁄2 years. In research, Nayak used his personal collection of film magazines and interviewed approximately 70 people, including her family members, her contemporaries and her friends. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Vishnu's Vaikuntha Chaturmukha form holding Gadadevi (right hand) and Chakrapurusha in his hands.
Ayudhapurusha is the anthropomorphic depiction of a divine weapon in Hindu art. Ayudhapurushas are sometimes considered as partial incarnates of their divine owners.
The sex of the personified weapon is determined by the gender of the weapon in the Sanskrit language. The suffix "purusha" (man) is added to masculine weapons and "devi" (goddess) to female ones. The weapons Shakti, Heti (a Hatchet-like weapon) and Gada (mace), especially Kaumodaki (the mace of Vishnu), Dhanus/Dhanushya ("bow") are women. Chakra, especially Vishnu's Sudarshana Chakra (discus of Vishnu), Shankha ("conch"), Padma (lotus), Ankusha (elephant goad), Pasha (noose), Trisula (trident), vajra (thunderbolt), Khadga (sword), Danda (a sceptre or club), Bana/Shara ("arrow") and Bhindi (sling) are depicted male. (Full article...) -
Image 3The 2020–21 season was the 101st season of Sporting Club East Bengal (EB or SCEB). Established in 1920, the club celebrated its centennial on 1 August 2020. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Indian football season started on 1 August 2020 and is scheduled to end on 31 May 2021, with competitive matches occurring between November and March. The club competed in the Indian Super League (ISL) for the first time and finished their first ISL season in ninth place with 17 points.
Before the start of the season, East Bengal was very active in the transfer market. The club precontracted over 20 Indian players with many signing long-term contracts and being assigned to the reserve team. Only a few players were retained from the previous season. Of them, Prakash Sarkar and Boithang Haokip were not registered in the ISL squad. East Bengal and Quess Corp's joint venture was terminated, and the club inked a partnership with Shree Cement as their principal investor in September. Robbie Fowler was appointed as the team's head coach. Forward Bright Enobakhare was signed in the winter transfer window as the seventh foreigner. Another foreign player, Callum Woods, was also signed as a reserve defender. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Tawang Monastery is a Buddhist monastery located in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh, India. It is the largest monastery in the country. It is situated in the valley of the Tawang Chu, in close proximity to the Chinese and Bhutanese border.
Tawang Monastery is known in Tibetan as Gaden Namgyal Lhatse, which translates to "the divine paradise of complete victory". It was founded by Merak Lama Lodre Gyatso in 1680–1681 in accordance with the wishes of the 5th Dalai Lama, Ngawang Lobsang Gyatso. It belongs to the Gelug school of Vajrayana Buddhism and had a religious association with Drepung Monastery of Lhasa, which continued during the period of British rule. (Full article...) -
Image 5In Hindu mythology, Asikni (Sanskrit: असिक्नी, romanized: Asiknī, lit. 'the dark one' or 'night'), also known as Panchajani and Virani, is a consort of Daksha in the Puranic pantheon. Most scriptures mention her as the mother of 6000 sons and 60 daughters. (Full article...)
-
Image 6Pitri Paksha rites being performed on the banks of the Hooghly River at Jagannath Ghat in Kolkata, 2012
Pitri Paksha (Sanskrit: पितृ पक्ष, lit. '"fortnight of the paternal ancestors"', IAST: Pitṛ pakṣa), also spelt Pitru Paksha, is a 16-lunar day period in the Hindu calendar when Hindus pay homage to their ancestors (Pitri), especially through food offerings. The period is also known as Pitarpas, Pitri Paksha/Pitr-Paksha, Pitri Pokkho, Sorah Shraddha ("sixteen shraddhas"), Kanagat, Jitiya, Mahalaya, Apara Paksha and akhadpak.
Pitri Paksha is considered by Hindus to be inauspicious, given the death rite performed during the ceremony, known as Shraddha or Tarpana. In southern and western India, it falls in the second paksha (fortnight) Hindu lunar month of Bhadrapada (September) and follows the fortnight immediately after Ganesh Utsav. It begins on the Pratipada (first day of the fortnight) ending with the no moon day known as Sarvapitri Amavasya, Pitri Amavasya, Peddala Amavasya or Mahalaya Amavasya (simply Mahalaya) Most years, the autumnal equinox falls within this period, i.e. the Sun transitions from the northern to the southern hemisphere during this period. In North India and Nepal, and cultures following the purnimanta calendar or the solar calendar, this period may correspond to the waning fortnight of the luni-solar month Ashvina, instead of Bhadrapada. (Full article...) -
Image 7Thiruvilaiyadal (transl. The Divine Game) is a 1965 Indian Tamil-language Hindu mythological film written, directed and co-produced by A. P. Nagarajan. The film stars Sivaji Ganesan, Savitri, and K. B. Sundarambal, with T. S. Balaiah, R. Muthuraman, Nagesh, T. R. Mahalingam, K. Sarangapani, Devika, Manorama, and Nagarajan in supporting roles. K. V. Mahadevan composed the film's soundtrack and score, and Kannadasan and Sankaradas Swamigal wrote the song lyrics.
Thiruvilaiyadal was inspired by the Thiruvilaiyadal Puranam: a collection of sixty-four Shaivite devotional, epic stories, written in the 16th century by Paranjothi Munivar, which record the actions (and antics) of Shiva on Earth in a number of disguises to test his devotees. Thiruvilaiyadal depicts four of the stories. The first is about the poets Dharumi and Nakkeerar; the second concerns Dhakshayani. The third recounts how Shiva's future wife, Parvati, is born as a fisherwoman; Shiva, in the guise of a fisherman, finds her and marries her. The fourth story is about the singers Banabhathirar and Hemanatha Bhagavathar. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Russell's viper (Daboia russelii) is a highly venomous snake in the family Viperidae native to South Asia. It was described in 1797 by George Shaw and Frederick Polydore Nodder. It is named after Patrick Russell and is one of the most dangerous big four snakes in India. (Full article...) -
Image 9P. labiata from Hong Kong
Portia labiata is a jumping spider (family Salticidae) found in Sri Lanka, India, southern China, Burma (Myanmar), Malaysia, Singapore, Java, Sumatra and the Philippines. In this medium-sized jumping spider, the front part is orange-brown and the back part is brownish. The conspicuous main eyes provide vision more acute than a cat's during the day and 10 times more acute than a dragonfly's, and this is essential in P. labiata′s navigation, hunting and mating.
The genus Portia has been called "eight-legged cats", as their hunting tactics are as versatile and adaptable as a lion's. All members of Portia have instinctive hunting tactics for their most common prey, but often can improvise by trial and error against unfamiliar prey or in unfamiliar situations, and then remember the new approach. While most jumping spiders prey mainly on insects and by active hunting, females of Portia also build webs to catch prey directly and sometimes join their own webs on to those of web-based spiders. Both females and males prefer web spiders as prey, followed by other jumping spiders, and finally insects. In all cases females are more effective predators than males. (Full article...) -
Image 10
The Telangana Rebellion, natively known as Telangana Sayudha Poratam, was a communist-led insurrection of peasants against the princely state of Hyderabad in the region of Telangana, Dominion of India, that escalated out of agitations in 1944–46.
Hyderabad was a feudal monarchy where most of the land was concentrated in the hands of landed aristocrats known as durras in Telangana. Feudal exploitation in the region was more severe compared to others of India; the durras had complete power over the peasants and could subject them to agricultural slavery. Conditions worsened during the 1930s due to the Great Depression and a transition towards commercial crops. In the 1940s, the peasants started turning towards communism, organised themselves through the Andhra Mahasabha and began a rights movement, catalyzed by a food crisis that affected the region following the end of the Second World War, the movement escalated into a rebellion after the administration and the durras attempted to suppress it. (Full article...) -
Image 11
Tapasee Pannu (born 1 August 1987), known as Taapsee Pannu, is an Indian actress who works primarily in Hindi, Telugu, and Tamil films. She has received two Filmfare Awards. After a brief modelling career, Pannu made her acting debut with the 2010 Telugu film Jhummandi Naadam and went on to act in the 2011 Tamil film Aadukalam. She made her Hindi film debut with David Dhawan's comedy Chashme Baddoor (2013). After playing the leading lady in several Telugu and Tamil films, Pannu gained notice for her performances in the Hindi spy thriller Baby (2015) and the courtroom drama Pink (2016), both of which were critical and commercial successes.
Pannu gained prominence in Hindi cinema with the war drama The Ghazi Attack (2017), the social drama Mulk (2018), the romantic drama Manmarziyaan (2018), the psychological thriller Badla (2019), and the space drama Mission Mangal (2019). For portraying the septuagenarian sharpshooter Prakashi Tomar in the biopic Saand Ki Aankh (2019), she won the Filmfare Critics Award for Best Actress, and for playing a homemaker going through a divorce in Anubhav Sinha's social drama Thappad (2020), she won the Filmfare Award for Best Actress. She has since starred in the streaming films Haseen Dillruba (2021), Rashmi Rocket (2021), Looop Lapeta (2022), and Phir Aayi Hasseen Dillruba (2024). Her highest-grossing release came in the comedy-drama Dunki (2023). (Full article...) -
Image 12
The 2008 attacks on Christians in southern Karnataka were the wave of attacks directed against Christian churches and prayer halls in the Indian city of Mangalore and the surrounding area of southern Karnataka in September and October 2008 by Hindu nationalist organisations such as Bajrang Dal and Sri Ram Sena. The attacks were widely perceived by Christians in southern Karnataka to be revenge from right-wing Hindu nationalist organisations, because Mangalorean Christians had been outspoken about the 2008 anti-Christian attacks in Orissa.
On 29 August, many groups across India participated in a "prayer for peace and communal harmony" in response to ongoing anti-Christian violence in Orissa. St Aloysius College and around 2000 Christian schools in Karnataka went on strike on 29 August, protesting against the attacks in Orissa. This was in defiance of orders of the government that 29 August was to be a regular work day. The BJP administration of Karnataka denounced local Christian institutions for disobeying orders in response, and a Bajrang Dal demonstration was held outside St Aloysius College. Strikes and protests continued for the next two weeks. The main attacks began on 14 September, when a group of youths from the Bajrang Dal went inside the chapel of Adoration Monastery of the Sisters of St Clare near the Milagres Church in Hampankatta and desecrated it. Some 20 churches, temples, and halls belonging to Catholic, Protestant, Jehovah's Witness, and independent Christians were attacked. Christian buildings were damaged across Mangalore taluk, Dakshina Kannada, Udupi and Chikkamagaluru districts. A few Christian institutions were later attacked in Bangalore district and Kasaragod district. (Full article...) -
Image 13Blue Pilgrims is an organised group of football fans who support the India national football men's team, women's team, and all the other age–group national teams at almost every home and away game. Founded in 2017 before the commencement of the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup, which was held in India, the group based their name on the nickname of the national team, the "Blue Tigers". They consider travelling with the national teams to wherever the teams play as their pilgrimage. They often display flags, banners, and tifos in support of the national team. (Full article...)
-
Image 14
Kartik Aaryan (né Tiwari; born 22 November 1990) is an Indian actor who works in Hindi films. While pursuing a degree in engineering, he made his acting debut with Luv Ranjan's buddy film Pyaar Ka Punchnama (2011). He went on to star in the romances Akaash Vani (2013) and Kaanchi (2014), but these failed to propel his career forward.
Aaryan had commercial successes in Ranjan's comedies Pyaar Ka Punchnama 2 (2015) and Sonu Ke Titu Ki Sweety (2018), his breakthrough film, as well as the romantic comedies Luka Chuppi and Pati Patni Aur Woh (both 2019). He also played against type in the thrillers Dhamaka (2021) and Freddy (2022), and the romantic drama Satyaprem Ki Katha (2023), and gained praise for portraying Murlikant Petkar in the biopic Chandu Champion (2024). His highest-grossing releases came with the comedy horror films Bhool Bhulaiyaa 2 (2022) and Bhool Bhulaiyaa 3 (2024). The former also earned him a nomination for the Filmfare Award for Best Actor. (Full article...) -
Image 15Dear Zindagi (transl. Dear life) is a 2016 Indian Hindi-language coming-of-age comedy drama film written and directed by Gauri Shinde. It was produced by Gauri Khan, Karan Johar, and Shinde under the banners of Red Chillies Entertainment, Dharma Productions, and Hope Productions, respectively. The film stars Alia Bhatt and Shah Rukh Khan in the lead roles with Ira Dubey, Kunal Kapoor, Angad Bedi, Ali Zafar (in his final Hindi film acting credit), Yashaswini Dayama and debutant Rohit Suresh Saraf in supporting roles. The plot centres on a budding cinematographer who is discontented with her life and meets a free-spirited psychologist who helps her to gain a new perspective on her life.
Development of the film began in 2015, when Shinde signed Bhatt and Khan for a film to be made under her banner. Principal photography took place in Goa and Mumbai, in the period from 21 January to 20 May 2016. The film features a score composed by Amit Trivedi and lyrics written mostly by Kausar Munir. (Full article...) -
Image 16Pandurangi Kodanda Rao (25 December 1889 – 23 July 1975) was an Indian social and independence activist who served as a member and secretary of the Indian socio-political organization Servants of India Society between 1922 and 1958. He was the private secretary to V. S. Srinivasa Sastri with whom he traveled as an advisor and delegate to multiple Round Table Conferences and other international conferences. Rao was also an associate of Indian freedom leader Mahatma Gandhi and assisted him in his campaigns against untouchability. Rao wrote extensively on topics including overseas Indians, emigration, immigration, and Indian politics under British rule. (Full article...)
-
Image 17
Jahanpanah was the fourth medieval city of Delhi established in 1326–1327 by Muhammad bin Tughlaq (reigned 1325–51) of the Delhi Sultanate. To counter the persistent threat of Mongol invasions, Tughlaq constructed the fortified city of Jahanpanah (meaning "Refuge of the World" in Persian), incorporating the Adilabad Fort, built in the 14th century, along with all the establishments located between Qila Rai Pithora and Siri Fort. Neither the city nor the fort has survived. Many reasons have been offered for such a situation. One of these is exemplified by the idiosyncratic rule of Mohammed bin Tughlaq, who inexplicably decreed the capital to be moved to Daulatabad in the Deccan, only to return to Delhi soon after.
The ruins of the city's walls are even now discerned in the road between Siri to Qutub Minar, and also in isolated patches behind the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), in Begumpur, Khirki Masjid, Satpula and many other nearby locations; at some sections, as seen at Satpula, the fort walls were large enough to have few inbuilt storerooms to stack provisions and armory. The mystery of the city's precincts (complex) has unfolded over the years with later day excavations revealing a large number of monuments in the villages and residential colonies of South Delhi. (Full article...) -
Image 18Kuch Kuch Hota Hai is a 1998 Indian Hindi-language musical romantic comedy drama written and directed by Karan Johar and produced by his father Yash Johar under Dharma Productions. It stars Shah Rukh Khan, Kajol, Rani Mukherji, Salman Khan and Sana Saeed. The plot combines two love triangles set years apart. The first half covers friends on a college campus, while the second tells the story of a widower's young daughter who tries to reunite her dad with his old best friend.
Filmed in India, Mauritius, and Scotland, Kuch Kuch Hota Hai was Karan Johar's directorial debut. One of his goals for the film was to set a new level for style in Hindi cinema. The music was composed by Jatin–Lalit, which was the biggest seller of the year. (Full article...) -
Image 19Tijori on the sets of Raja Natwarlal, 2014
Deepak Tijori (born 28 August 1961) is an Indian film director and actor who works in Bollywood and Gujarati films and is well known for his supporting roles in Aashiqui (1990), Khiladi (1992), Jo Jeeta Wohi Sikandar (1992), Kabhi Haan Kabhi Naa (1994), Ghulam (1998) and Baadshah (1999). He also starred as a lead actor in Pehla Nasha (1993). Tijori started his directing career with Oops! (2003), a film about male strippers. This was followed by Fareb (2005), Khamoshh... Khauff Ki Raat (2005), Tom, Dick, and Harry (2006) and Fox (2009). Thriller at 10 – Fareb, a TV mini-series produced by Tijori won the 2001 Indian Television Academy Awards in the category best mini-series. His recent directorial, Do Lafzon Ki Kahani, was released in the year 2016. (Full article...) -
Image 20Jagadguru Rambhadracharya delivering a sermon on 25 October 2009 in Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, India
Jagadguru Ramanandacharya Swami Rambhadracharya (born Pandit Giridhar Mishra on 14 January 1950) is an Indian Hindu spiritual leader, educator, Sanskrit scholar, polyglot, poet, author, textual commentator, philosopher, composer, singer, playwright and Katha artist based in Chitrakoot, India. He is one of four incumbent Jagadguru Ramanandacharya, and has held this title since 1988.
Rambhadracharya is the founder and head of Tulsi Peeth, a religious and social service institution in Chitrakoot named after Saint Tulsidas. He is the founder and lifelong chancellor of the Jagadguru Rambhadracharya Handicapped University in Chitrakoot, which offers graduate and postgraduate courses exclusively to four types of disabled students. Rambhadracharya has been blind since the age of two months, had no formal education until the age of seventeen years, and has never used Braille or any other aid to learn or compose. (Full article...) -
Image 21Kadhalikka Neramillai (transl. No Time for Love) is a 1964 Indian Tamil-language romantic comedy film produced and directed by C. V. Sridhar, who also conceived and co-wrote its script with Chitralaya Gopu. The film features an ensemble cast consisting of Balaiah, Muthuraman, Nagesh, Rajasree, Sachu, Ravichandran and Kanchana. The latter two made their acting debut with this film.
The plot of Kadhalikka Neramillai revolves around Viswanathan, an estate owner who hopes to get his daughters Nirmala and Kanchana married to wealthy grooms. However, Nirmala falls in love with Ashok, a poor man who was once employed by Vishwanathan. To earn Viswanathan's approval, Ashok pretends to be the only heir of a rich businessman; he is supported by his friend Vasu, who poses as Ashok's fictional millionaire father Chidambaram. A comedy of errors ensues when Vasu discovers his lover Kanchana is Viswanathan's other daughter. (Full article...) -
Image 22

The 1960 North Indian Ocean cyclone season featured two deadly tropical cyclones that collectively killed approximately 20,000 people collectively in East Pakistan (present-day Bangladesh). The Indian subcontinent divides the North Indian Ocean into two areas: the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre for this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories. On average, five storms form in the North Indian Ocean every season with dual peaks in activity during May and November. Cyclones that occurred between 45°E and 100°E were included in seasonal records by the IMD.
Fifteen depressions developed during the 1960 season, with five becoming cyclonic storms. The majority of the activity took place in the Bay of Bengal, where eleven systems formed; however, the season's first storm formed over the Arabian Sea on May 10. The storm produced hurricane-force winds and attained a barometric air pressure of 974 mbar (hPa; 28.76 inHg). The deadliest and most intense cyclone of the season was Severe Cyclonic Storm Ten, which killed 14,174 in East Pakistan in early November. With peak winds estimated at 150 km/h (95 mph) and a pressure of 966.7 mbar (hPa; 28.55 inHg), it struck just three weeks after the previous system devastated the same area. The storm produced a 6.1 m (20 ft) storm tide that swept 16 km (10 mi) inland, submerging several small islands. The two storms left a combined 200,000–300,000 people homeless. These systems marked the start of an unusually active period of cyclones impacting East Pakistan, culminating ten years later with the 1970 Bhola cyclone, which killed between 300,000 and 500,000 people. During the 1960 season, several depressions impacted India with heavy rainfall. Collectively, these systems killed 167 people. (Full article...) -
Image 23Chandramukhi (transl. Moon-faced lady) is a 2005 Indian Tamil-language psychological horror comedy film written and directed by P. Vasu. It is a remake of Vasu's Kannada film Apthamitra (2004) which itself is based on the Malayalam film Manichitrathazhu (1993).The film stars Rajinikanth, Prabhu and Jyothika along with an ensemble supporting cast, including Vadivelu, Nayanthara, Nassar and Sheela. It revolves around a woman who suffers from dissociative identity disorder that affects a family, and a psychiatrist who intends to solve the case while risking his life.
Chandramukhi was produced by Prabhu and his brother Ramkumar Ganesan through their company Sivaji Productions, and is the company's 50th film. The soundtrack album and background score were composed by Vidyasagar. Cinematography was handled by Sekhar V. Joseph and editing was done by Suresh Urs. Principal photography began on 24 October 2004 and was completed in March 2005. (Full article...) -
Image 24The University of Calcutta, informally known as Calcutta University (CU), is a public state university located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. It has 151 affiliated undergraduate colleges and 16 institutes in Kolkata and nearby areas. It was established on 24 January 1857 and is the oldest multidisciplinary university of Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asian Region. Today, the university's jurisdiction is limited to a few districts of West Bengal, but at the time of its establishment it had a catchment area ranging from Kabul to Myanmar. It is accredited as an "A" grade university by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC).
The university has a total of fourteen campuses spread over the city of Kolkata and its suburbs. As of 2020, 151 colleges and 21 institutes and centres are affiliated with CU. The university was fourth in the Indian University Ranking 2021 list, released by the National Institutional Ranking Framework of the Ministry of Education. (Full article...) -
Image 25
The Pundarikakshan Perumal Temple or Thiruvellarai Temple in Thiruvellarai, a village in the outskirts of Tiruchirappalli in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu, is dedicated to the Hindu god Vishnu. Constructed in the Dravidian style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Naalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th–9th centuries CE. It is one of the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu, who is worshipped as Pundarikakshan and his consort Lakshmi as Pankajavalli.
According to legends, the temple is said to have been built by Sibi Chakravarthy. The temple has three inscriptions in its two rock-cut caves, two dating from the period of Nandivarman II (732–796 CE) and the other to that of Dantivarman (796–847). It also has Pallava sculptural depictions of Narasimha and Varaha, two of the ten avatars of Vishnu. (Full article...)
News
- 15 November 2024 –
- Ten infants are killed and 16 others are injured in a fire inside a neonatal intensive care unit at the Jhansi Medical College hospital in Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh, North India. (AP)
- 13 November 2024 – 2024 Indo-Pakistani smog
- New Delhi, India, reports its 15th consecutive day with a "very poor" recorded air quality index due to significant air pollution causing zero meter visibility smog. (The Hindu)
- 13 November 2024 – Bulldozer Justice
- The Supreme Court of India rules that it is unconstitutional for the government to demolish property belonging to people suspected of crimes without a legal process, a practice common in states ruled by the Bharatiya Janata Party. (The Times of India) (DW)
- 4 November 2024 – 2024 Almora bus accident
- At least 36 people are killed and 27 others are injured when a bus plunges into a gorge near Marchula, Uttarakhand, India. (The Indian Express) (ABC News)
- 3 November 2024 – Insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir
- At least eleven people are injured in a grenade explosion caused by an unknown militant group in a flea market in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India. (Reuters)
Did you know...
- ... that in 1884 Motibai Kapadia's father allowed her to study alongside men in India?
- ... that when visiting Britain during World War II, naval officer Kalyani Sen reported that Indian women were breaking down prejudices against men and women working together by joining the military?
- ... that before becoming a commissioner of Indian affairs, William P. Dole was only known to have encountered Native Americans once in his life?
- ... that according to Indian chef Imtiaz Qureshi, who is credited with reviving the cooking tradition of dum pukht, all biryanis are pulaos?
- ... that a judge is threatening to shut down Wikipedia in India over a defamation lawsuit?
- ... that Indian aristocrat and photographer Umrao Singh Sher-Gil left more than 3000 prints and negatives, including many of his daughter Amrita Sher-Gil, documenting life in Europe and India?
Topics related to India
Timeline of Indian history, Indus Valley Civilisation, Dholavira, Science and technology in ancient India, Meluhha, Aryan invasion theory, Out of India theory, Greek conquests in India, Indian maritime history, Maurya Empire, Ashoka, Shunga Empire, Hoysala Empire, Vijayanagara, Satavahana dynasty, Indo-Greek Kingdom, Indo-Scythians, Indo-Parthian Kingdom, Kushan Empire, Western Satraps, Gupta Empire, Chola dynasty, Pala Empire, Islamic incursions in India, Mughal Empire, Maratha Empire, British Raj, East India Company, Governor-General, Viceroy, War of Independence, 1857, Indian independence movement, Indian National Army, Azad Hind, Quit India Movement, Partition of India, History of Republic of India, Non-Aligned Movement, Sino-Indian War, Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948, Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, Kargil War, 2001–02 India–Pakistan standoff, Military, Demographic
Law, Hindu law, Constitution, Political parties (Indian National Congress, Bharatiya Janata Party), Foreign relations, Elections, Political divisions, Reservation in India
Government agencies, Legislative branch (Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha) Executive branch (President & Vice President, Prime Minister & Deputy Prime Minister, Cabinet Ministers, Cabinet Secretary, Election Commission, Foreign Minister; Law enforcement: CBI, CID, Intelligence: IB, RAW), Directorate General of Income Tax Investigation Judicial branch (Supreme Court), Armed Forces (Army, Navy, Air Force, Border Security Force, Coast Guard)
Himalayas, Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats, Indo-Gangetic Plain, Deccan Plateau, Thar Desert, Ganges, Rann of Kutch, Brahmaputra River, Northeast India; Mountains, Valleys, Islands, Rivers; States and union territories, Cities, Districts, Regions, Fauna, Flora
Rupee, Bombay Stock Exchange, National Stock Exchange, Standard of living, Companies, Reserve Bank of India, Energy policy (Solar, Wind, Nuclear), Tourism, Transport (Expressways, Rail transport, Auto rickshaw),
Languages, Standard of living, Religion
Music (Carnatic, Hindustani, Indi-pop), Dance, Languages, Literature, Architecture, Film & TV, Cuisine, Holidays, Folklore, Education, Media, Indian martial arts
Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Indian Institute of Astrophysics, National Centre for Software Technology, AIIMS, IISc, IIT, NIT, BITS-Pilani, INRegistry, Indian numbering system, Indian Space Research Organisation, National Internet Exchange of India, ICRISAT, International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad
Indian English, Indian nationality law, Numbering system, Indian Space Research Organisation, Telecommunications, National Highways Development Project, Flag, Vehicle registration plates, Indian nationalism, Metrication in India
Categories
Related portals
Religions in India
Indian Subcontinent
Other countries
Wikipedias in Indian languages
- অসমীয়া (Assamese)
- বাংলা (Bengali)
- भोजपुरी (Bhojpuri)
- বিষ্ণুপ্রিয়া মণিপুরী (Bishnupriya Manipuri)
- गोंयची कोंकणी / Gõychi Konknni (Konkani)
- ગુજરાતી (Gujarati)
- हिन्दी (Hindi)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- कॉशुर/كشميري (Kashmiri)
- मैथिली (Maithili)
- മലയാളം (Malayalam)
- मराठी (Marathi)
- नेपाली (Nepali)
- नेपाल भाषा
- (Newari)
- ଓଡ଼ିଆ (Odiya)
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ (Punjabi)
- पालि (Pali)
- संस्कृत (Sanskrit)
- ᱥᱟᱱᱛᱟᱲᱤ (Santali)
- سنڌي (Sindhi)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ತುಳು (Tulu)
- اردو (Urdu)
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- Pages with Bengali IPA
- Pages with Hindustani IPA
- Pages with Hindi IPA
- Pages with non-numeric formatnum arguments
- Portals with triaged subpages from June 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 51–100 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 501–1000 articles in article list
- Wikipedia move-protected portals
- Redirect targets of redirected portals with existing subpages
























































































